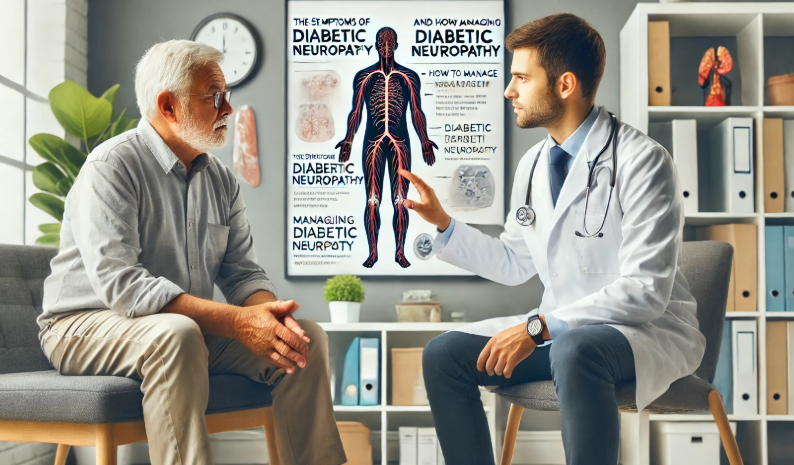
Living with diabetes often requires careful management to prevent complications, including diabetic neuropathy. This condition is a result of long-term diabetes, affecting the nerves and leading to a variety of symptoms that may impact daily life. Understanding this condition, its causes, symptoms, and management techniques can help in navigating this complex condition.
What Is Diabetic Neuropathy?
Diabetic neuropathy refers to nerve damage caused by prolonged high blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes. This nerve damage may develop over time, making it a complication of both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. It can affect different parts of the body, but it most commonly impacts the extremities, particularly the legs and feet.
There are different types of diabetic neuropathy, such as peripheral, autonomic, proximal, and focal neuropathies. Each type affects different nerves and causes varying symptoms. Consulting a doctor helps with diagnosis and treatment.
What Causes It?
These nerve issues develop due to a combination of factors linked to diabetes. Elevated blood sugar levels sustained over time are one of the primary causes. High glucose can damage the walls of tiny blood vessels that supply nutrients and oxygen to the nerves, leading to dysfunction. Additional factors include chronic inflammation associated with diabetes, genetic predisposition, and other health issues such as high cholesterol or high blood pressure.
What Are the Symptoms?
The symptoms of diabetic neuropathy may vary based on the type of nerves affected. Below are some common signs individuals might experience:
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Often starting in the feet and hands, this type can cause numbness, tingling, or burning sensations.
- Autonomic Neuropathy: This type affects the autonomic nerves controlling involuntary functions and causes digestive issues, bladder problems, or dizziness when standing.
- Proximal Neuropathy: This form typically impacts the thighs, hips, or buttocks, leading to sudden, severe pain or weakness in these areas.
- Focal Neuropathy: Affecting specific nerves, it can cause sudden weakness, pain, or difficulty in movement or eyesight.
What Treatments Help With Management?
Managing diabetic neuropathy focuses on reducing symptoms and slowing further progression. While nerve damage cannot always be reversed, several strategies can make living with the condition more manageable:
- Injection Therapy: Some clinics offer nerve block injections to alleviate pain in affected areas. This treatment may provide temporary relief for localized discomfort.
- Pain-Relieving Medications: Certain prescription medications may be recommended for managing nerve pain. These medications target the nerves responsible for discomfort.
- Regular Exercise: Activities like walking, swimming, or yoga can improve blood flow, strengthen muscles, and reduce some symptoms. Physical activity may also help in stabilizing blood sugar levels, providing additional benefits.
- Alternative Treatments: Some people explore non-traditional methods like acupuncture, which may alleviate symptoms for specific individuals. Consult a healthcare provider before beginning alternative therapies.
Why Should You Seek Help?
Ignoring the symptoms of diabetic neuropathy may lead to further complications. Numbness in the extremities, for instance, may increase the risk of injuries or infections. Autonomic issues, such as those affecting digestion or the cardiovascular system, can also impact overall health if left untreated. Consulting a healthcare professional allows for a personalized approach to managing the condition.
Learn More Today
Diabetic neuropathy can be challenging, but effective strategies exist to help manage symptoms and improve well-being. Understanding the condition, its causes, and available treatments is the first step toward finding relief. If you’re experiencing any symptoms or looking to explore management options further, connect with a healthcare provider today.